Personnel Management of the Government
Personnel Management of the Government
Util Menu
Key Features
- Handling of presidential appointments of state civil servants recommended by each ministry and agency
- Handling of presidential appointments and dismissal of civil servants of constitutional institutions, heads and auditors of public institutions, others in the positions appointed by the President, members of government committees, etc.
- Requests for the National Assembly’s consent to appointments and personnel confirmation hearing, presentation of the government’s proposal for appointment at the Cabinet meeting, conferment ceremonies for certificates/letters of appointment issued by the President
Legal Grounds
- Constitution: Article 78
- State Public Officials Act: Article 32 (Appointment Authorities)
- Decree on the Appointment of Public Officials: Article 5 (Delegation of Authority for Appointment)
-
Regulations on the Personnel Management of the Senior Executive Service: Article 5 (Delegation of Authority to Appoint)
* Presidential Orders for Appointment (for Civil Servants in General Service)
- Transfer, suspension from a position, temporary retirement, suspension of a duty, reinstatement and holding of concurrent posts of a senior civil servant at deputy minister level
- Recruitment, promotion, change of jobs, appointment to a lower rank, demotion, inter-agency transfer and holding of concurrent posts (under the jurisdictions of different competent ministers), dismissal, release and removal from office of a civil servant or an official of a higher position
- Personnel Records/Statistics on Civil Servants and Regulations on the Handling of Personnel Affairs Management
- Organization of the Ministry of Personnel Management and Its Affiliated Agencies: Article 12
Appointment Procedures
- Government personnel appointments are delivered through the following procedures: recommendation by competent ministers and consultation with the Minister of Personnel Management (MPM), passing through the Prime Minister and the final appointment by the President; recruitment of civil servants in general service and in extraordinary civil service who are part of the senior civil service, promotion of civil servants in general service to SCS positions, etc. need to undergo the MPM’s personnel screening in advance.
- Handling Process

- [Procedures Required for Appointment of Key Positions]
-
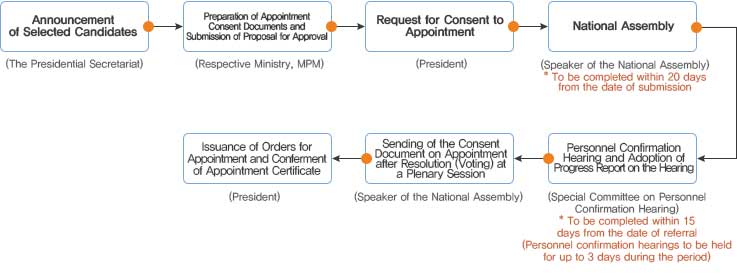
- The National Assembly’s Consent to Appointment
Pursuant to Articles 86, 98, 104 and 111 of the Constitution, 17 persons, including the Prime Minister, the Chair of the Board of Audit and Inspection, the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court and 13 Justices of the Supreme Court and the Chief Justice of the Constitutional Court are appointed with the consent of the National Assembly.
The National Assembly’s Consent to Appointment and Appointment Procedures
- Number of Positions Elected by the National Assembly: six (three of the Justices of the Constitutional Court; three of the members of the National Election Commission)
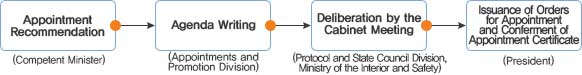
- Deliberation by the Cabinet Meeting
- When appointed, the Prosecutor General, the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, the Chief of Staff of each armed forces, presidents of national universities, ambassadors, generals of each armed forces (at the time of promotion), the Governor of the Bank of Korea, etc. must undergo deliberation by the Cabinet meeting pursuant to Subparagraph 16, Article 89 of the Constitution, Paragraph 3, Article 25 of the Military Personnel Management Act, Paragraph 1, Article 33 of the Bank of Korea Act, etc.
- The National Assembly’s Consent to Appointment